Reverse osmosis (RO) or hyperfiltration, is a separation process that uses applied pressure to force a solvent through a semi-permeable membrane. The applied feed pressure, which is greater than the fluid’s osmotic pressure, causes water (or other solvent) molecules to pass through the semi-permeable membrane to the dilute side of the membrane contrary to normal osmotic flow.
Salts and other contaminants cannot pass through the membrane and hence, concentrate up on the retentate side of the membrane as per Figure 1.
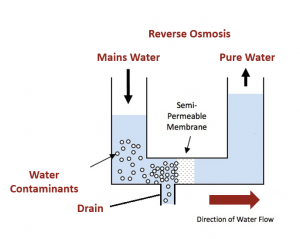
Figure 1: Reverse Osmosis process
RO membranes act as a barrier to flow for all dissolved salts, inorganic molecules and all organic molecules with a MW > 100 g/mol. Water molecules pass freely through the membrane allowing for rejection of dissolved salts in the concentrate of between 95 – 99% of feed concentrations. Actual salt rejection depends on factors like membrane design, feed composition, temperature and system design.
RO membranes are poly amide (PA) based allowing for a broader operational tolerance for pH and temperature. Modern membrane construction is a tri-layer thin film composite comprising a polyester support matrix, an intermediate microporous polysulfone layer and an ultra-thin polyamide top layer. Feed pressures to RO systems range from 2-17 bar(g) for fresh water & brackish streams to 40 – 70 bar(g) for sea water desalination in order to overcome the solution osmotic pressure.
Typical RO applications include waste water treatment and polishing in the power generation, food and beverage, dairy, pharmaceutical, chemical manufacture, oil and gas industry sectors.
RO also finds ever-increasing application as a final stage polisher unit where water recovery is a primary consideration. Extra pure water applications (e.g., pharma, semi-conductor manufacture) also require multiple RO stages.







